The pharmaceutical industry is amid a transformative era, witnessing profound changes in its commercial landscape.
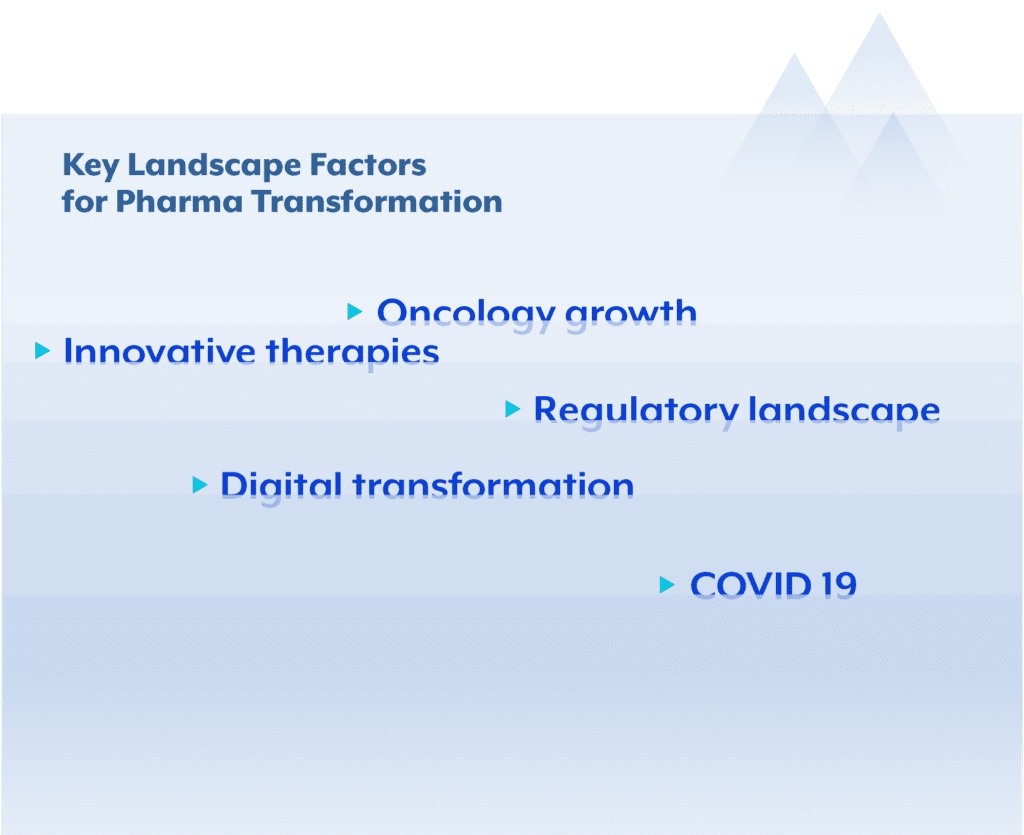
Key drivers for this transformation include the ascendancy of oncology as the largest therapeutic area in both sales and research and development (R&D) investments, the growing importance of biologics, gene therapies, and digital therapeutics, the evolving regulatory landscape emphasizing privacy, compliance, and healthcare cost reduction and, not less important, the digital transformation and the covid 19 pandemic.
The commercial approach of pharmaceutical companies, long characterized by traditional practices, is struggling to adapt to this new environment.
The goal of this article is to provide a view on what factors are driving the change in commercial strategies, and the potential impact these changes might have on the industry’s future.
The oncology revolution
One of the most notable changes in the pharmaceutical industry is the overwhelming dominance of oncology. The rapid growth in cancer-related therapeutics has made oncology the largest therapeutic area in terms of both revenue and R&D spending. This shift can be attributed to several factors:
- Precision medicine: The emergence of precision medicine has led to targeted therapies that offer higher efficacy with fewer side effects. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in developing drugs that cater to specific genetic mutations, allowing for more precise and effective treatments.
In some situations, specially on orphan drugs, governments are even supporting research and commercialization. This allows for these areas to finally be viable to pharma.
- Immunotherapies: The rise of immunotherapies, including checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapies, has revolutionized cancer treatment. These therapies have shown remarkable success in a variety of cancer types, further driving investments and research in the field.
- Market potential: As the global cancer burden continues to rise, oncology drugs present significant market potential. The broadening patient populations and expanding indications for existing therapies have fuelled commercial interest.
Innovative therapies: biologics, gene therapies, and digital therapeutics
One other key factor for the “revolution” is its increasing prominence of biologics, gene therapies, and digital therapeutics:
- Biologics: Monoclonal antibodies and other biologic drugs are becoming integral in treating various diseases. Their complexity, high cost, and manufacturing intricacies have driven pharmaceutical manufacturers to adapt to new production processes and regulatory standards.
- Gene therapies: Gene editing and gene therapies hold promise in addressing genetic disorders and rare diseases. While they offer revolutionary treatments, accessibility, pricing, and long-term patient monitoring remain challenging issues.
- Digital therapeutics (DTx): The intersection of software and pharmacology has given rise to digital therapeutics. These innovative solutions can augment traditional drug therapies, offering patients personalized health management tools. However, navigating regulatory challenges and data privacy concerns is a pivotal challenge.
Evolving regulatory landscape
The regulatory landscape is also undergoing significant shifts with a focus on privacy, compliance, and healthcare cost reduction:
- Privacy and data security: The protection of patient data and adherence to data privacy regulations have become paramount. GDPR, HIPAA, and similar regulations necessitate stringent compliance, which in turn affects patient trust and industry transparency.
- Compliance and quality assurance: Ensuring drug safety and adherence to regulatory standards is non-negotiable. Quality control, especially in the biologics sector, has become an essential aspect
of commercial operations to mitigate the risks of contamination and recalls. - Cost reduction and healthcare access: The challenge of pharmaceutical pricing and market access is prompting the industry to explore new pricing models such as value-based pricing and outcomes-based agreements. The industry must balance innovation with cost control to ensure affordable access to medicines. Although some minor movement on this area is already seen, there is still a long way to go, and pharma must be open to use and develop real world insights and data gathering to achieve it.
Digital transformation
Digital transformation in the pharmaceutical industry is not merely a technological upgrade; it represents a fundamental rethinking of how healthcare is delivered, managed, and experienced. Pharma is now starting to explore emerging trends in pharmaceutical digital transformation, including the integration of Internet of Things (IoT), 5G technology, and the potential impact of quantum computing on drug discovery.
- Research and development: In the era of big data and artificial intelligence, pharmaceutical companies are leveraging advanced analytics to expedite drug discovery processes. Machine learning algorithms analyse vast datasets, helping identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy, thereby reducing research timelines and costs.
- Manufacturing and supply chain: Digital technologies are optimizing manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. Blockchain is emerging as a game-changer in the supply chain, providing transparency, traceability, and security, which are paramount in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Regulatory compliance: The pharmaceutical sector operates within a highly regulated environment. Digital transformation is streamlining compliance processes, facilitating real-time monitoring, and ensuring adherence to evolving regulatory standards. Electronic batch records and digital validation processes are becoming industry norms.
- Marketing and sales: Pharmaceutical companies need to embrace digital channels for marketing and sales, leveraging data-driven insights to personalize interactions with healthcare professionals and consumers. Digital marketing strategies, including social media engagement and targeted advertising, are redefining the industry’s communication landscape.
- Patient engagement and healthcare delivery: The focus on patient-centric care is driving innovations in digital health. Mobile apps, wearable devices, and telemedicine are fostering better patient engagement, monitoring, and adherence to treatment plans. Digital tools are enabling remote patient monitoring, reducing hospitalization rates, and improving overall healthcare outcomes. Pharma is transitioning from a product-centric to a patient-centric approach, leveraging digital tools to deliver value beyond the pill.
- Cybersecurity and data privacy: As digital transformation accelerates, concerns around data security and privacy become paramount. The challenges and strategies for safeguarding sensitive healthcare data, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures and ethical data practices needs to be considered.
The Covid 19 spark
The pharmaceutical industry was at the forefront of the battle against COVID-19, swiftly adapting to unprecedented challenges. As the dust settles, the pharma sector does not need just to emerge intact; needs to evolve. The commercial approach of pharmaceutical companies, long characterized by traditional practices, is undergoing a major transformation.
- Agility: The pandemic forced the industry to revamp its traditional commercial playbook. Lockdowns, restrictions, and changing healthcare dynamics meant that the age-old practices of sales reps physically visiting healthcare professionals had to adapt or give way. Virtual engagement, powered by technology, emerged as a viable alternative. Webinars, virtual conferences and calls, and online symposiums provided a means for disseminating information and establishing relationships without geographical constraints. Post-COVID, this virtual component is likely to remain an integral part of the commercial approach, offering convenience and reach that transcends borders.
- Redefining sales models: The days of one-size-fits-all sales models are numbered. The pandemic prompted a revaluation of sales approaches, resulting in a more targeted and flexible strategy. Companies are shifting towards solution-based selling, addressing the specific challenges faced by healthcare providers. Instead of merely pushing products, pharma companies are positioning themselves as partners in patient care, offering comprehensive solutions that extend beyond the medication.
- Elevated focus on patient support: The pandemic revealed the significance of patient support programs. With healthcare systems strained and patients facing difficulties accessing healthcare facilities, pharma companies stepped in to offer support. This approach is transcending the pandemic, with companies investing in patient assistance programs, disease management platforms, and educational resources. In a post-COVID world, these initiatives will be essential not only for patient well-being but also as a means of building trust and loyalty.
- Healthcare equity and accessibility: The pandemic’s unequal impact underscored the importance of healthcare equity. Post-COVID, pharma companies are recognizing their role in ensuring equitable access to medications and treatments. Pricing strategies are being reconsidered, and collaborations are being forged to ensure that underserved populations are not left behind. This commitment to equitable healthcare is reshaping the commercial approach to align with broader societal values.
The future of pharmaceutical commercialization
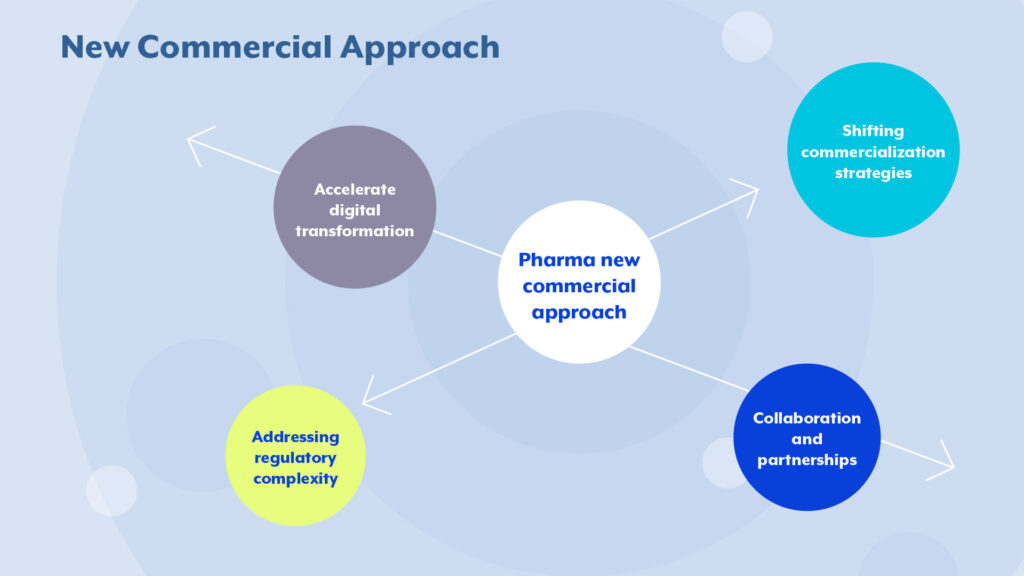
As pharmaceutical manufacturers navigate these transformative changes, several key considerations for the future emerge:
Shifting commercialization strategies: The dominance of oncology and the rise of innovative therapies require tailored commercialization strategies. Patient-centric approaches and digital engagement will play a pivotal role in success.
Collaboration and partnerships: The industry is increasingly leaning on cross-industry partnerships to address healthcare costs. Collaborative R&D initiatives and public-private partnerships will drive global health access.
Addressing regulatory complexity: Navigating the complex and evolving regulatory landscape is essential. Investment in regulatory and compliance expertise, and advocacy for policies that support innovation while ensuring affordability, will be critical.
Accelerate digital transformation: Embracing digital transformation will help the pharmaceutical industry to stay competitive, innovate faster, and ultimately deliver better healthcare solutions.
In conclusion, the pharmaceutical industry’s commercial landscape is undergoing an unprecedented transformation. To thrive in this dynamic environment, pharmaceutical companies must adapt their commercialization strategies, prioritize patient-centric approaches, and engage in collaborative efforts to balance innovation, access, and cost control. The future of the industry holds immense potential for advancements in patient care and public health, as long as pharma embraces the needed transformation.